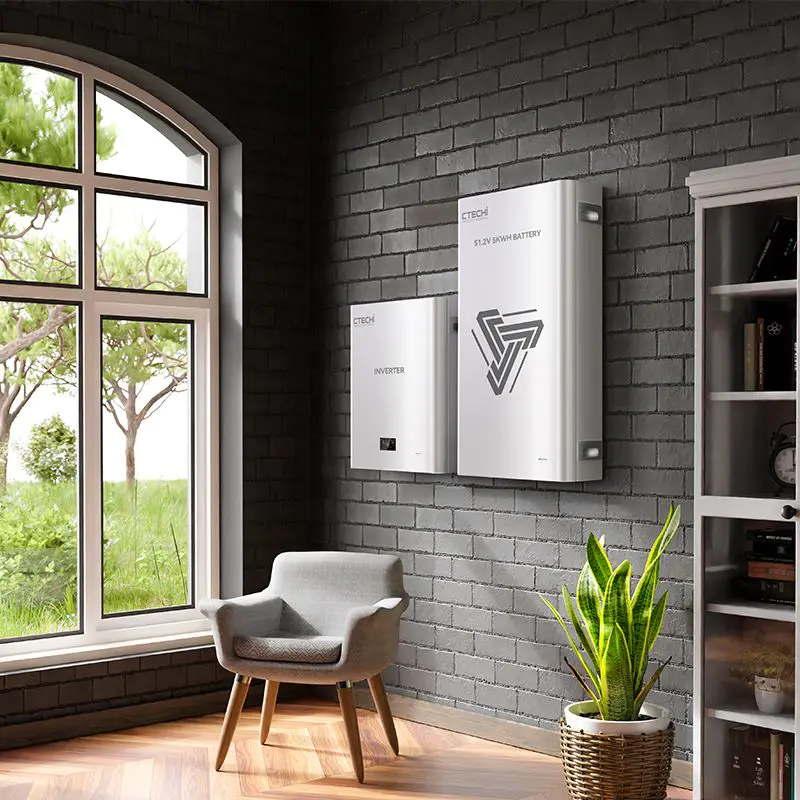
South Korea has developed new materials for lithium batteries is expected to promote the development of secondary batteries
Lithium Grid News: The Korean Research Consortium announced that the institute has jointly developed a new binder anode material with high voltage and high capacity in conjunction with Chungnam University and Kim U University of Technology, which has greatly increased the energy of secondary lithium batteries. density. The research results were published in the international academic journal 'Advanced Functional Materials' (Advanced Functional Materials).
Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LiCoO2) and Nickel Cobalt Manganese (NCM) currently used have limited capacity, and a larger capacity anode material is required. As a new generation of anode materials, lithium-rich manganese oxide has attracted much attention. It has twice the energy capacity of lithium cobalt oxide oxide, but high capacity can only be obtained by increasing the charging voltage above 4.4V. However, in this case, the secondary battery will generate heat, which will weaken the viscosity of the adhesive and cause problems such as weakened battery performance.
South Korea is committed to the development of high-energy-density secondary batteries. The anode material developed by the research group is a binder material that forms a protective film on the surface of the electrode under the conditions of a high voltage of 4.7V and a high temperature of 55 degrees to maintain a stable interface. It does not require additional electrolyte additives and can also maintain a stable viscosity. The lithium cobalt oxide used has more than twice the capacity and more stable charge and discharge performance. The research team said that this technology can further promote the development of secondary lithium batteries.
Share to: